Configuring SSH GIT in Talend Administration Center
Before you begin
Procedure
-
Go to your /.ssh directory, for example
/home/<username>/.ssh for Linux and
C:\Users\<username>\.ssh for Windows.
Create the folder if it does not exist.
$ cd /.ssh -
Execute the command ssh-keygen to generate authentication keys for
SSH.
The ssh-keygen command is used to generate, manage, and convert authentication keys for SSH.The specific command ssh-keygen -t rsa-sha2-512 -m includes options to generate an RSA key with a SHA-2 512-bit signature and specify the key format. You can
- Open a Terminal.
To use ssh-keygen, you need to have a terminal or command-line interface open. This can be on a Unix-based system (Linux, macOS) or on Windows using Git Bash or Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
- Execute the following command to generate the
key:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa-sha2-512 -m PEMssh-keygen allows to generate SSH keys.
-t rsa-sha2-512 specifies the type of key to create. In this case, it is an RSA key with SHA-2 512-bit signature. rsa is the correct option for specifying an RSA key type. rsa-sha2-512 specifies the signature algorithm, which is used during the authentication.
-m PEM specifies the key format. PEM stands for Privacy-Enhanced Mail, a base64 encoded format with header and footer lines.
- Save the key by pressing Enter to accept the default
location (/home/your_username/.ssh/id_rsa), or providing a custom
path.
Enter file in which to save the key (/c/Users/emmap1/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/c/Users/emmap1/.ssh'. - For the passphrase, keep it empty by pressing
Enter.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: - You can see two files after
completion.
Your identification has been saved in /c/Users/emmap1/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /c/users/emmap1/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: e7:94:d1:a3:02:ee:38:6e:a4:5e:26:a3:a9:f4:95For the private key, the file you saved (id_rsa by default) contains your private key.
For the public key, the file with the same name but with a .pub extension (id_rsa.pub by default) contains your public key.
If you save the public/private keys with other name, such as gitkey/gitkey.pub, you need to use and configure the SSH config file.
Location of the SSH Config File: The SSH configuration file is typically located at ~/.ssh/config. If this file does not exist, you can create it.
File Permissions: Ensure that the config file has the correct permissions. It should be readable and writable only by the owner:$ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/configBasic Structure of the SSH Config File: The SSH config file uses a simple syntax to define settings for each host. Here is an example of what the file might look like:Host github.com (https://github.com) IdentityFile ~/.ssh/gitkeywhere Host github.com is the actual hostname or IP address of the server you are connecting to and IdentityFile ~/.ssh/gitkey is the path to the private key file to use for authentication.
Information noteNote: The space before and after IdentityFile is required, do not delete this.
- Open a Terminal.
-
Access https://dev.azure.com/ to
create your account, then click SSH public keys on the right
top of page.
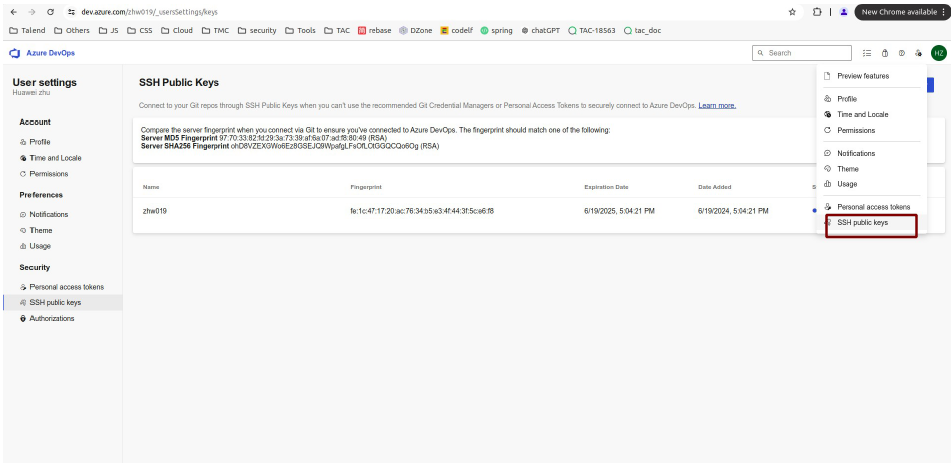
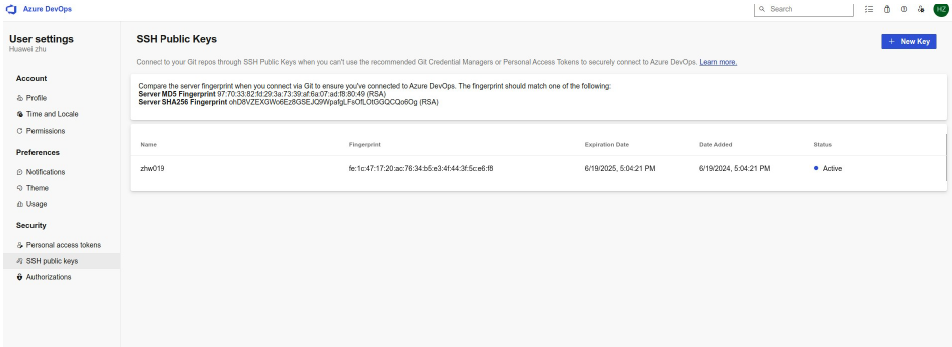
- Click the New Key button to set your public key.
-
Copy/paste the public key content from the previous file generation, by default
id_rsa.pub for example.
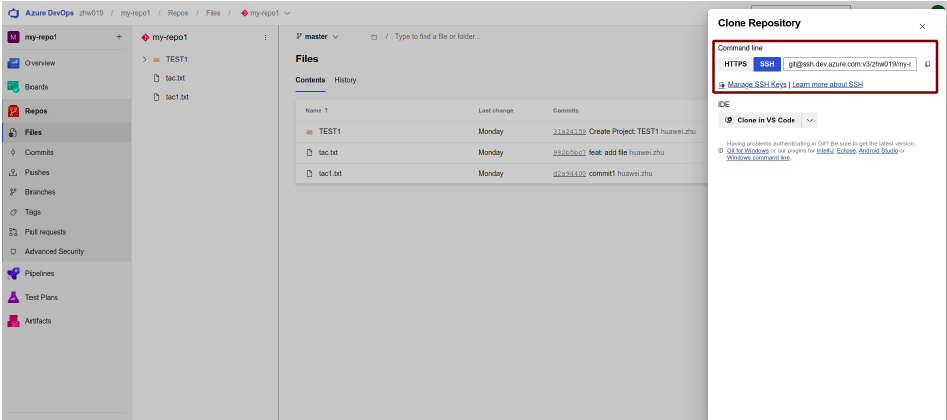
- Go back to your Azure repository page.
-
Copy the SSH URL using the ssh-keyscan command utility to add your
SSH host keys to your ~/.ssh/known_hosts file.
$ ssh-keyscan -H ssh.dev.azure.com >> known_hostsWhere -H means hash all hostnames and addresses in the output.This can help to prevent from attacks by ensuring that you are connecting to the correct server. -
Copy/paste the SSH URL into the Git server url field in the
Configuration page of TAC, for example
ssh://git@dev.azure.com:v3/account/my-repo1.
 Keep the username and password fields empty.You can see a green check when it is successful.
Keep the username and password fields empty.You can see a green check when it is successful.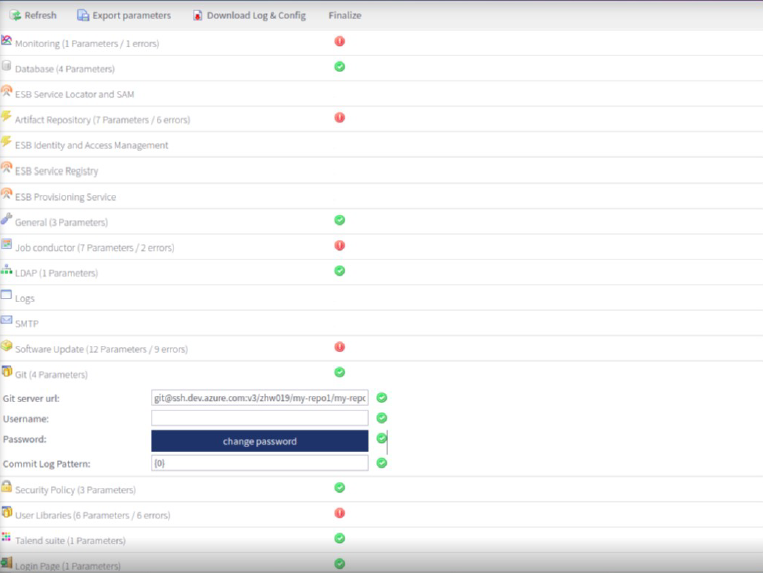
Did this page help you?
If you find any issues with this page or its content – a typo, a missing step, or a technical error – please let us know!
