Creating a numerical correlation analysis
Before you begin
About this task
Information noteRestriction: The numerical correlation analysis is possible only on database
columns. You can not use this analysis on file connections.
Defining the numerical correlation analysis
Procedure
Results
Selecting the columns you want to analyze and setting analysis parameters
Procedure
Results
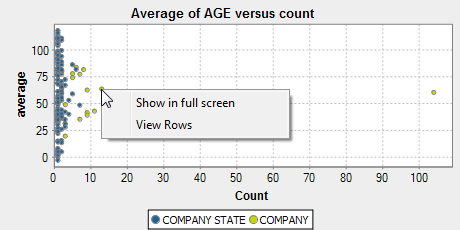
For more information about the analysis results, see Exploring the results of the numerical correlation analysis.

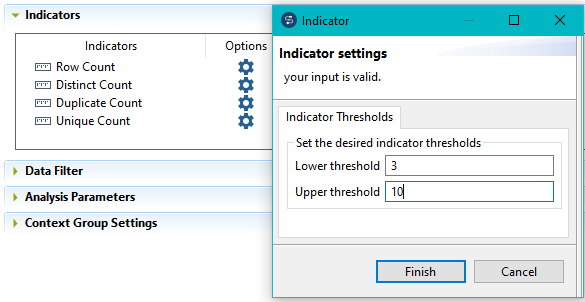
 to open a dialog box where you can set thresholds for each indicator.
to open a dialog box where you can set thresholds for each indicator.