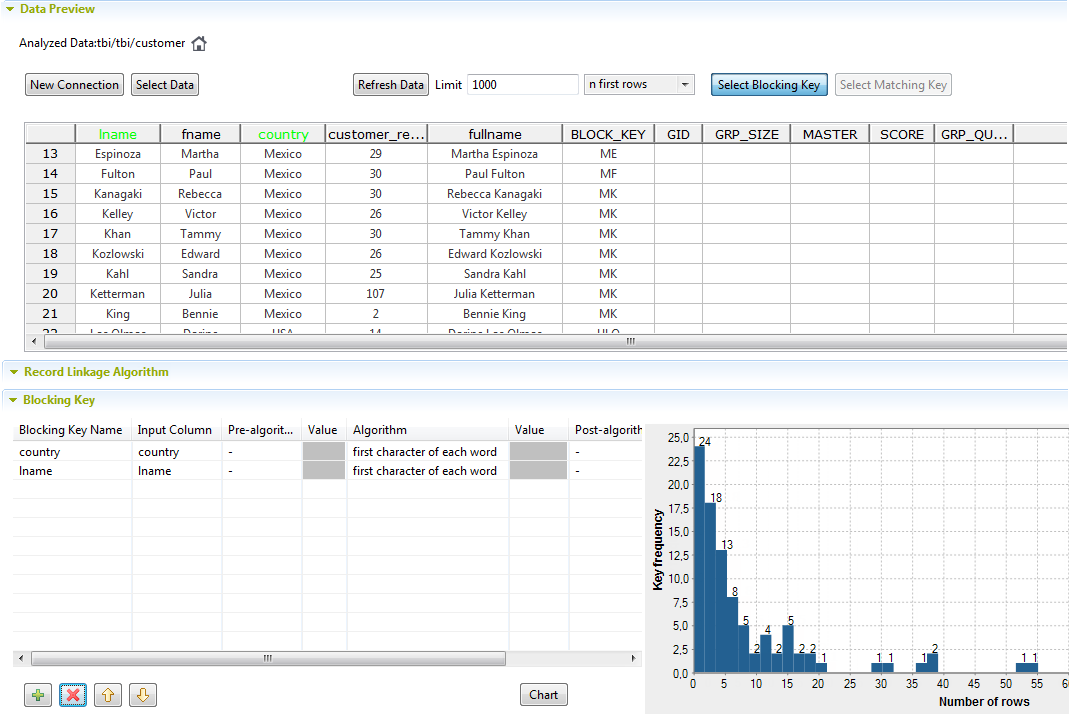
About this task
Defining a blocking key is not mandatory but strongly advisable. Using a blocking key to
partition data in blocks reduces the number of records that need to be examined as
comparisons are restricted to record pairs within each block. Using blocking columns is
very useful when you are processing a big dataset.
-
In the Data section, click the Select Blocking
Key tab.
-
Click the name of the columns you want to use to partition the processed data in
blocks.
Blocking keys that have the exact name of the selected columns are listed in the
Blocking Key table.
You can define more than one column in the table, but only one blocking key will
be generated and listed in the BLOCK_KEY column in the
Data table.
For example, if you use an algorithm on the country and
lnamecolumns to process records that have the same first
character, data records that have the same first letter in the country and last names
are grouped together in the same block. Comparison is restricted to record within
each block.
To remove a column from the Blocking key table, right-click
it and select Delete or click on its name in the
Data table.
-
Select an algorithm for the blocking key, and set the other parameters in
the Blocking Key table as needed.
In this example, only one blocking key is used. The first character of
each word in the country column is retrieved and listed
in the BLOCK_KEY column.
-
Click Chart to compute the generated key,
group the sample records in the Data table
and display the results in a chart.
This chart allows you to visualize the statistics regarding the number of
blocks and to adapt the blocking parameters according to the results you
want to get.