Running a Route built as a Spring Boot Microservice (deprecated)
This section will show you how to run a Route that is built as a Spring Boot based Microservice.
To run a Route that is exported as a .jar file, proceed as follows in a console window:
-
Change to the directory where the Microservice .jar file is located.
-
Type in the following command. For more information about the Spring Boot properties, see the documentation. Note that not all of the properties listed on the web page are applicable to the ESB Microservice. It depends primarily on the features that are included by Talend and also the Routes you build.
java -jar <ArchiveFileName> --<SpringBootProperty>For example, the following command executes a Microservice named demoRoute.0.1.jar using an environment property that is configured in the file Prod, where Prod is also the Talend context name. This parameter needs to be specified to switch between context properties.
java -jar demoRoute.0.1.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:config/contexts/ --spring.config.name=ProdBy default, when running the Microservice Route, it calls the configuration files in the /config folder inside the Microservice jar. You can switch to an external configuration folder where the configuration files are located using the spring.config.additional-location property. For example, the following command executes the Microservice named demoRoute.0.1.jar using the configuration files in the config folder in the directory where the Microservice jar is located.
java -jar demoRoute.0.1.jar --spring.config.additional-location=./config
Spring Boot includes a number of built-in endpoints for you to monitor and interact with the Microservice. You can use the mappings endpoint to show the list of all available endpoints. For more information, see Spring Boot documentation.
To run a Route that is exported as a .zip file, proceed as follows:
-
Extract the .zip file in the directory of your choice.
-
Go to the <RouteName> folder that contains the external config folder, the Microservice .jar file, and the start scripts to start the Microservice for Linux (.sh) and Windows (.bat).
-
Edit the configuration files in the config folder as needed and run the .sh file on Linux or the .bat file on Windows to start the Microservice with the external configurations.
If the Route contains the cSOAP or cREST component, and if one or more of the ESB infrastructure services are used, you need to do the following when running the Microservice Route:
-
If the Service Activity Monitor is enabled, start the Service Activity Monitoring Server in a Runtime container before running the Microservice Route. For more information, see Installing the Service Activity Monitoring Server in a Runtime container.
-
If the Service Locator is enabled, start the Service Locator Server in a Runtime container before running the Microservice Route. For more information, see Installing and running the Service Locator Server in a Runtime container.
-
If the Route is a service provider and the Authentication with HTTP Basic is enabled, specify the user credentials when running the Microservice Route:
java -jar <ArchiveFileName>.jar --security.user.name=<USERNAME> -- security.user.password=<PASSWORD> -
If the Authentication with the SAML Token is enabled, you need to start the STS service in a Runtime container before running the Microservice Route. For more information, see Using STS with the Talend Runtime.
-
If the Authentication with the SAML Token, and Authorization is enabled, before running the Microservice Route,you need to:
-
install and start the Talend Identity Management Service, and create users and roles in it. For more information, see Installing and configuring Talend Identity and Access Management and Talend Identity and Access Management.
-
start the STS service in a Runtime container. For more information, see Using STS with the Talend Runtime.
-
start the Authorization service in a Runtime container. For more information, see Starting and stopping the Authorization service in the Talend Runtime Container.
-
start the Talend Administration Center and configure the XACML policy in the Authorization page. For more information, see Authorization with Talend ESB.
-
-
If the Service Registry is used, you need to:
-
start the related infrastructure service according to the WS-Policy in use. For more information, see Service Registry.
-
start the Talend Administration Center, and add the service WSDL and the WS-Policy into the Service Registry from the Service Registry page. For more information, see Accessing the Service Registry page.
-
Microservices built with Talend Studio provide access to Spring boot actuator endpoints. The default monitoring endpoints are limited to info, health and jolokia.
The basic authentication is always activated to reach the Microservice management endpoints (info, health and jolokia).
You need to setup the SPRING_BOOT_SECURITY_USER_NAME and SPRING_BOOT_SECURITY_USER_PASSWORD environment variables in the machine where the Microservice will be executed.
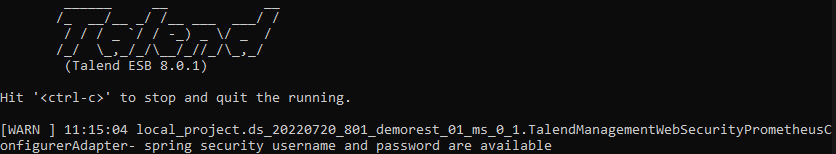
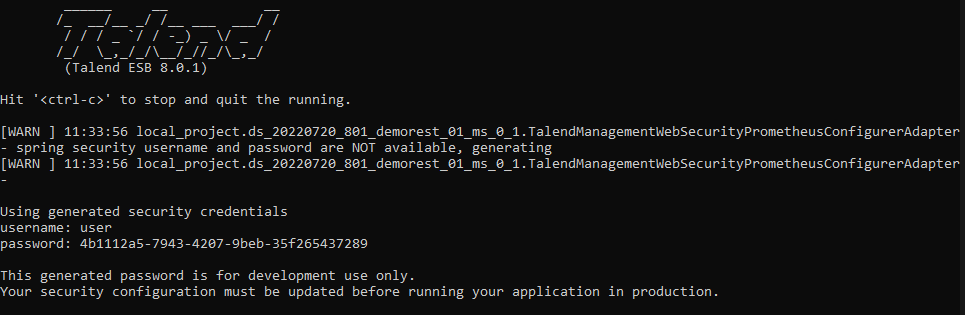
You will be prompted to sign in with the security credentials to access the Microservice management endpoints.
docker run -p 8065:8065 -t --env SPRING_BOOT_SECURITY_USER_NAME='user' --env SPRING_BOOT_SECURITY_USER_PASSWORD='password' p1/docker_ms_demorestroute