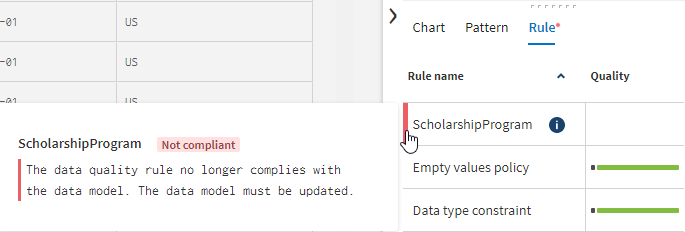
Filtering tasks using rules
The Rule tab of the profiling area shows all validation constraints and data quality rules used by the data model. A validation constraint represents each defined parameter of an attribute: the type, the minimum/maximum values, the precision, the validation pattern, the date, time and if empty values are allowed. When a parameter is defined, each value of the attribute is validated against this constraint. For example, minimum value is 3.
This tab allows you to know the number and percentage of:
- Valid, empty and invalid values for each validation constraint. The empty values are taken into account if Allow empty values is enabled for the attribute. When the setting is disabled, if the constraint is fulfilled, the value is valid. Otherwise, the value is invalid.
- Valid, non-applicable and invalid values for each data quality rule. The non-applicable values are the values that do not fulfill the condition of the data quality rule.