Modeling the accident-prone areas in a city
Before you begin
-
The Spark version to be used is 1.4 onwards.
-
The sample data is stored in your Hadoop file system and you have proper rights and permissions to at least read it.
-
Your Hadoop cluster is properly installed and is running.
If you are not sure about these requirements, ask the administrator of your Hadoop system.
-
In the Spark Configuration tab in the Run view, define the connection to a given Spark cluster for the whole Job. In addition, since the Job expects its dependent jar files for execution, you must specify the directory in the file system to which these jar files are transferred so that Spark can access these files:
-
Yarn mode (Yarn client or Yarn cluster):
-
When using Google Dataproc, specify a bucket in the Google Storage staging bucket field in the Spark configuration tab.
-
When using HDInsight, specify the blob to be used for Job deployment in the Windows Azure Storage configuration area in the Spark configuration tab.
- When using Altus, specify the S3 bucket or the Azure Data Lake Storage for Job deployment in the Spark configuration tab.
-
When using on-premises distributions, use the configuration component corresponding to the file system your cluster is using. Typically, this system is HDFS and so use tHDFSConfiguration.
-
-
Standalone mode: use the configuration component corresponding to the file system your cluster is using, such as tHDFSConfiguration Apache Spark Batch or tS3Configuration Apache Spark Batch.
If you are using Databricks without any configuration component present in your Job, your business data is written directly in DBFS (Databricks Filesystem).
-
About this task
-
This scenario applies only to subscription-based Talend products with Big Data.
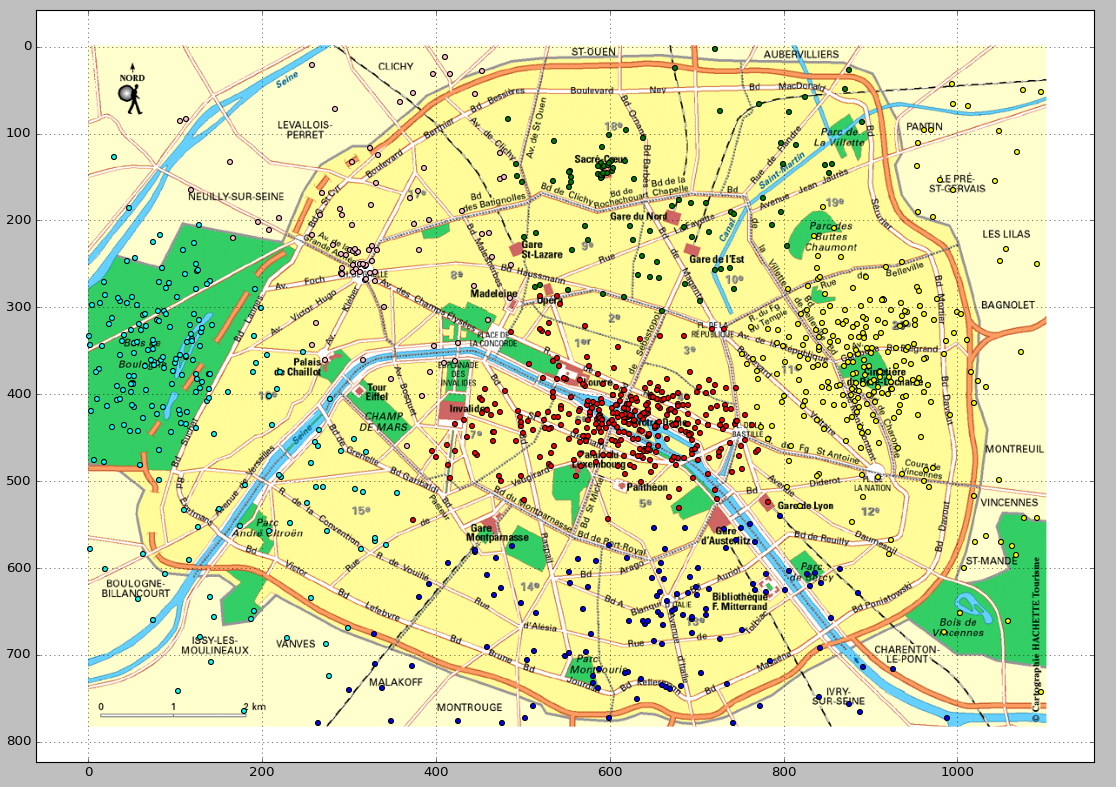
- A model like this can be employed to help determine the optimal locations for building hospitals.
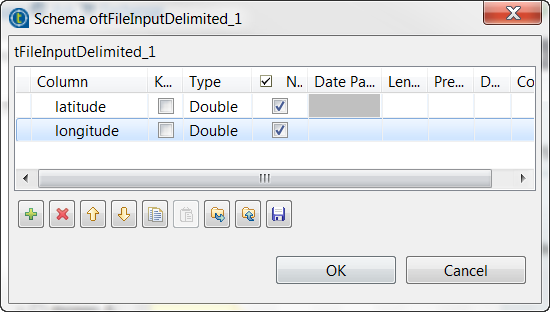
- The sample data consists of pairs of latitudes and longitudes. It was randomly and automatically generated for demonstration purposes only and in any case it does not reflect the situation of these areas in the real world.
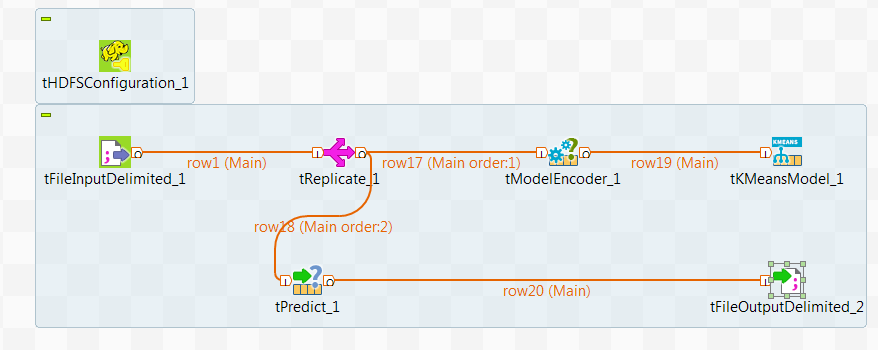
- The components to be used are:
-
tFileInputDelimited: it loads the sample data into the data flow of the Job.
-
tReplicate: it replicates the sample data and caches the replication.
-
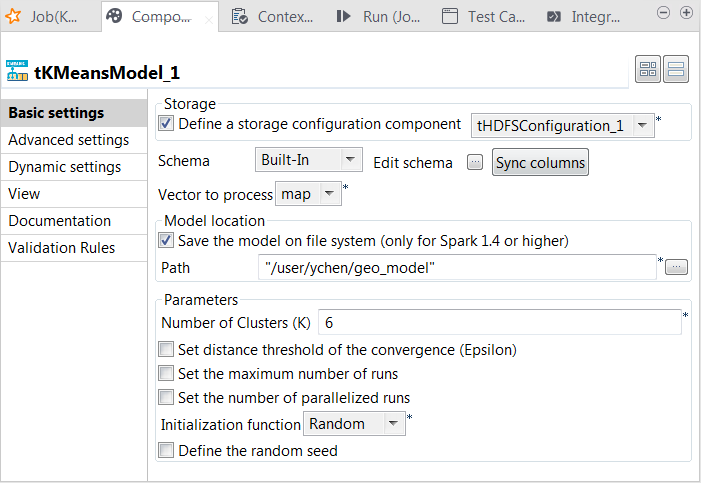
tKMeansModel: it analyzes the data to train the model and writes the model to HDFS.
-
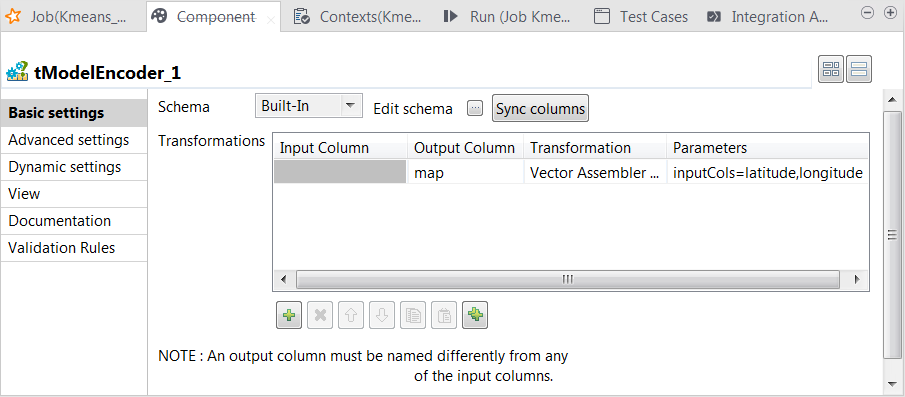
tModelEncoder: it pre-process the data to prepare proper feature vectors to be used by tKMeansModel.
-
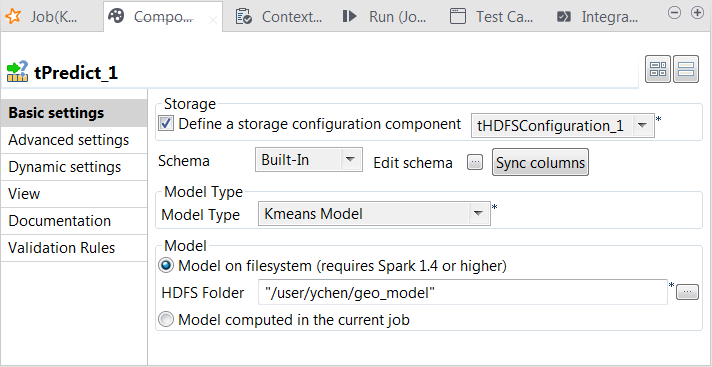
tPredict: it applies the KMeans model on the replication of the sample data. In the real-world practice, this data should be a set of reference data to test the model accuracy.
-
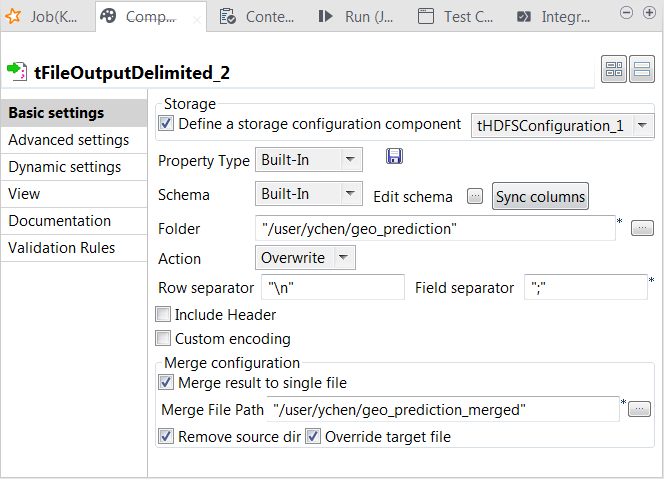
tFileOutputDelimited: it writes the result of the prediction to HDFS.
-
tHDFSConfiguration: this component is used by Spark to connect to the HDFS system where the jar files dependent on the Job are transferred.
-
Arranging data flow for the KMeans Job
Procedure
- In the Integration perspective of Talend Studio, create an empty Job from the Job Designs node in the Repository tree view.
- In the workspace, enter the name of the component to be used and select it from the list that appears.
- Connect tFileInputDelimited to tReplicate using the Row > Main link.
- Do the same to connect tReplicate to tModelEncoder and then tModelEncoder to tKMeansModel.
- Repeat the operations to connect tReplicate to tPredict and then tPredict to tFileOutputDelimited.
- Leave tHDFSConfiguration as it is.
Configuring the connection to the file system to be used by Spark
Reading and caching the sample data
Procedure
Preparing features for KMeans
Procedure
Testing the KMeans model
Procedure
Selecting the Spark mode
Executing the Job
Procedure
Results
The following image shows an example of the predicted clusters. This visualization is produced via a Python script. You can download this script from here and bear in mind to adapt the path in the script to access the prediction result in your own machine.