Writing and reading data from MongoDB using a Spark Batch Job
This scenario applies only to subscription-based Talend products with Big Data.
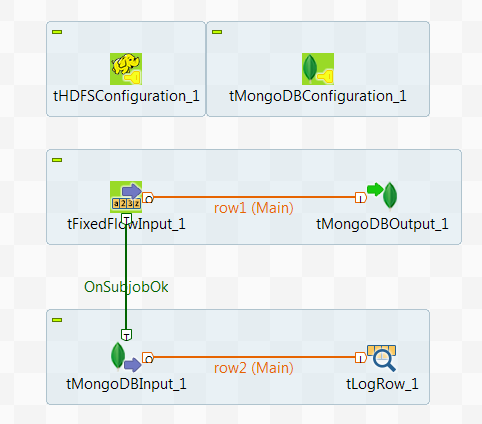
In this scenario, you create a Spark Batch Job to write data about some movie directors into the MongoDB default database and then read the data from this database.
1;Gregg Araki
2;P.J. Hogan
3;Alan Rudolph
4;Alex Proyas
5;Alex SichelThis data contains the names of these directors and the ID numbers distributed to them.
Note that the sample data is created for demonstration purposes only.
tHDFSConfiguration is used in this scenario by Spark to connect to the HDFS system where the jar files dependent on the Job are transferred.
-
Yarn mode (Yarn client or Yarn cluster):
-
When using Google Dataproc, specify a bucket in the Google Storage staging bucket field in the Spark configuration tab.
-
When using HDInsight, specify the blob to be used for Job deployment in the Windows Azure Storage configuration area in the Spark configuration tab.
- When using Altus, specify the S3 bucket or the Azure Data Lake Storage for Job deployment in the Spark configuration tab.
-
When using on-premises distributions, use the configuration component corresponding to the file system your cluster is using. Typically, this system is HDFS and so use tHDFSConfiguration.
-
-
Standalone mode: use the configuration component corresponding to the file system your cluster is using, such as tHDFSConfiguration Apache Spark Batch or tS3Configuration Apache Spark Batch.
If you are using Databricks without any configuration component present in your Job, your business data is written directly in DBFS (Databricks Filesystem).
Prerequisite: ensure that the Spark cluster and the MongoDB database to be used have been properly installed and are running.
To replicate this scenario, proceed as follows:
